Industries
Norm Additive is an advanced technology company operating to provide production and engineering support to the manufacturing, medical, machinery and aviation sectors, especially the automotive main industry and suppliers.

01

Automotive
Additive manufacturing has been embraced by the automotive industry as a rapid prototyping technology for many years. However, in the span of the last decade, the use of metal AM for serial production in automotive began to be explored, and 3D printers have moved from an optional piece of equipment for producing relatively simple prototypes to an absolute necessity. Automotive manufacturers are increasingly required to create adaptable bodywork designs that are economical to manufacture, and flexible to integrate a diverse range of drive types and energy storage systems, while reducing manufacturing costs and the overall weight. Additive manufacturing provides customization solutions across all aspects of the vehicle development process, driving efficiency and productivity from design to the manufacturing floor. A.M in automotive industry is currently used in scalable design, tooling, design customization, inspection and conformance.
02

Tooling
In the automotive industry alone, the production of tooling components for can result in months of development time and an expenditure of hundreds of thousands of dollars. Designing and manufacturing customized tools, fixtures, jigs and molds is the undisputed most expensive aspect of the production process. Furthermore, a damaged tool or a necessity to redesign a fixture delays the entire production cycle. Additive manufacturing is an invaluable technology for the rapid easy production of customized tooling in just a matter of hours instead of weeks as compared with conventional methodologies. In molding industry, strengths of metal additive manufacturing lie principally within the conformal cooling solutions. Additive manufacturing makes it possible to produce built-in cooling channels in the most complex designs, thus helps achieving reduced design time, lower production costs and better part quality as compared to conventional methods of mold manufacturing. The use of Additive Manufacturing to produce molds, tools and tooling components improves accuracy and reduces lead times as well as costs. Additionally, it improves part functionality and provides design freedom to customize products.
03
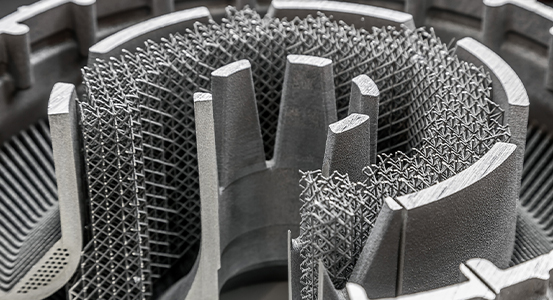
Machinery
Recent advancements in additive manufacturing technology have made it more accessible and feasible to be utilized in the manufacturing of industrial machinery. Main advantages of using 3D printing for machinery manufacturing are higher product development speed and supply chain efficiency, lower set-up costs and waste reduction. In machinery, unlike applications of other industries, product release is multi-stage process. Within this new product introduction process, production engineers constantly search for ways to reduce the production costs of the machine, exploring alternative ways for fabricating parts with the goal of improving profit margins. The mass production quota of an industrial machine typically consists of few hundreds or several thousands of components. This scale of production is an optimal one for many 3D printing solutions, since almost any successful cost reduction effort obtained in the early phases will also be achieved on the mass production scale. Opting for 3D printing instead of traditional manufacturing methods can be an extremely beneficial way to reduce manufacturing costs and accelerate time to market.
04

Medical
Today the global medical industry is one of the largest users of additive manufacturing. Advantages of additive manufacturing in complex design freedom and personalization can truly be utilized in medical industry, since this technology provides extensive customization as per the individual patient, ability of creating organic shapes and rapid low-volume manufacturing of each particular item. Surgeons can use data taken from MRI and CT scans to manufacture 3D printed models and practice surgery techniques. Using scans taken from the actual patient’s mouth, dentists and dental laboratories are able to build accurate and tailored solutions to fix dental problems. Patient specific implants can be very expensive and time consuming to make using traditional manufacturing techniques but with additive manufacturing they can be produced quickly and precisely in massively reduced time lines.
05
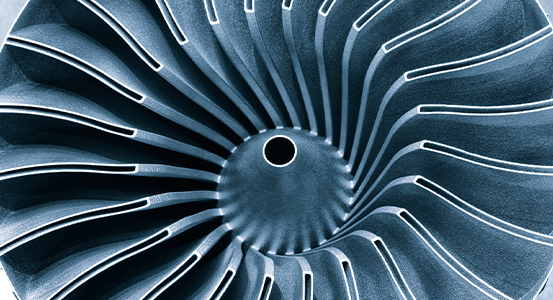
Aerospace
Technical and economic objectives of manufacturing in the aerospace sector are functional performance, lead-time reduction, light weighting, complexity, cost management, and sustainment. Each of these objectives must be considered carefully when selecting an optimal design solution. Additive manufacturing has a number of fundamental opportunities in aerospace applications including significant cost and lead-time reductions, unique design solutions, mass reduction of components through highly efficient and lightweight designs, and consolidation of multiple components for performance enhancement or risk management. Common examples are internal cooling features in thermally loaded components or elimination of traditional joining processes. These opportunities are already adopted in a range of commercial high-profile aerospace applications including liquid-fuel rocket engines, propellant tanks, satellite components, heat exchangers, turbomachinery and valves. Additive manufacturing allows the rapid prototyping and conceptual design review and validation, skipping tooling manufacture steps to go straight to finished parts. This enables engineers to test multiple configurations, find out customer preferences, minimize product-launch risk, and reduce overall lead-time. Additive manufacturing provides near-net shape parts and allows increasing design complexity without inflating manufacturing costs. This is doubtlessly the main advantage of the technology for aerospace industry in order to maximize performance, to consolidate designs and improve reliability and to achieve fuel efficiency. Additive manufacturing can also be effective in reducing warehousing and obsolescence costs by allowing on-demand and on-site manufacturing of spares.

Contact Us
Contact us to get information about the products and services we offer in the field of additive manufacturing.
Contact Form